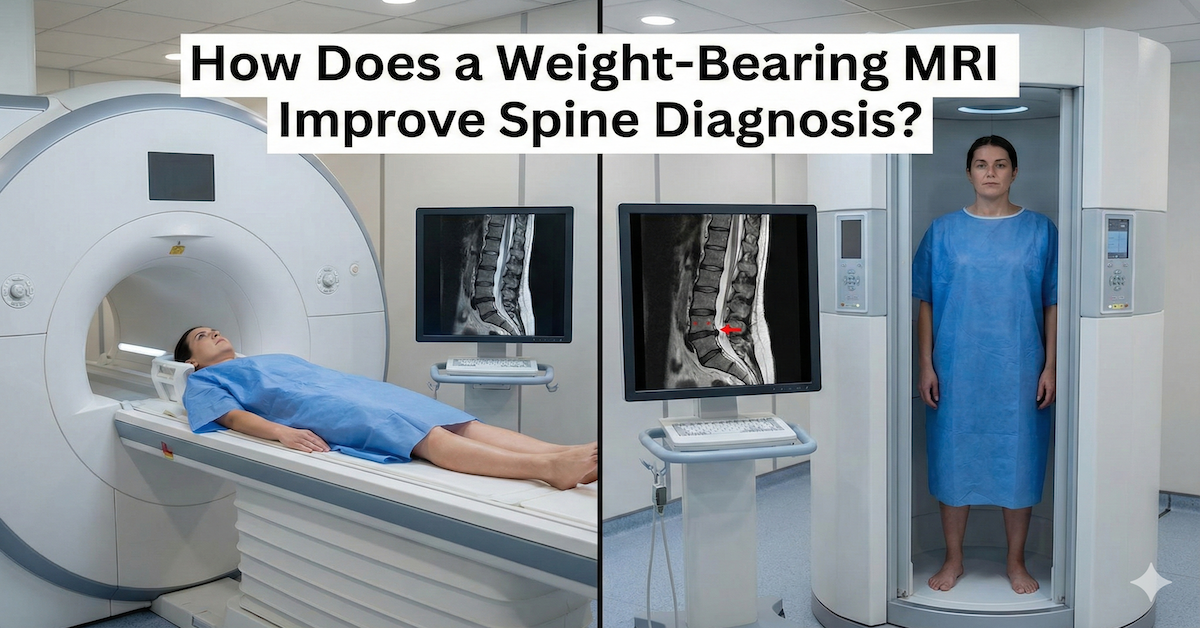
How Can I Interpret MRI Back and Spine Results?
MRI technology has revolutionized how we diagnose and understand spine and back issues. While getting an MRI can be straightforward, interpreting the results often isn't. This guide will help you make sense of your MRI back and spine results, so you can have a more informed discussion with your healthcare provider.
Basics of MRI Technology
MRIs (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) use powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRIs don’t use radiation. They’re especially useful for imaging soft tissues, like muscles and discs, making them ideal for back and spine issues.
Understanding MRI Reports
When you receive your MRI report, it might feel like reading a foreign language. These reports are structured and filled with medical jargon. Here’s a breakdown of what you can expect:
- Patient Information: Your name, date of birth, and other identifying details.
- Indications for the Scan: Why the MRI was performed, such as lower back pain or suspected herniated disc.
- Imaging Technique: Details on the specific MRI sequences used, like T1, T2, and STIR.
Anatomy of the Spine
Understanding basic spine anatomy helps when looking at your MRI results. The spine is divided into three main sections:
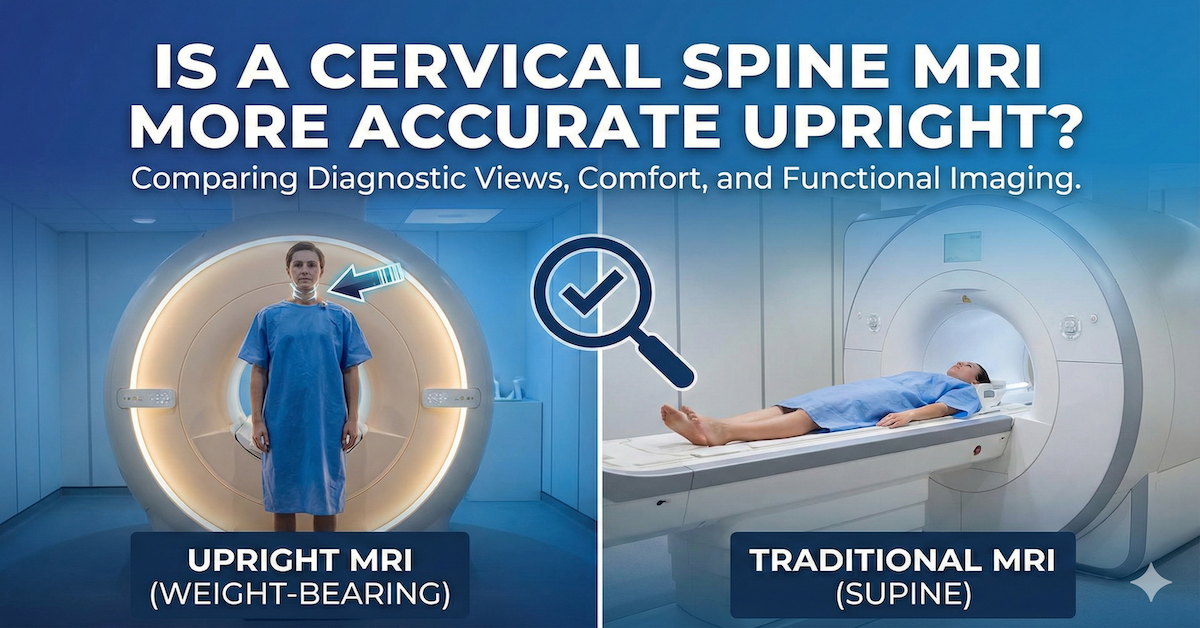
- Cervical (neck)
- Thoracic (mid-back)
- Lumbar (lower back)
Each section contains vertebrae, intervertebral discs, the spinal cord, nerve roots, ligaments, and muscles. Recognizing these structures on an MRI can help you understand the report better.
Common Findings on MRI
Degenerative Changes: These are normal parts of aging but can cause pain and discomfort.
- Disc Degeneration and Bulging: Discs lose hydration and height, leading to bulging.
- Herniated Discs: A more severe form of disc bulging where the inner disc material protrudes out.
- Facet Joint Arthritis: Wear and tear on the joints that connect vertebrae.
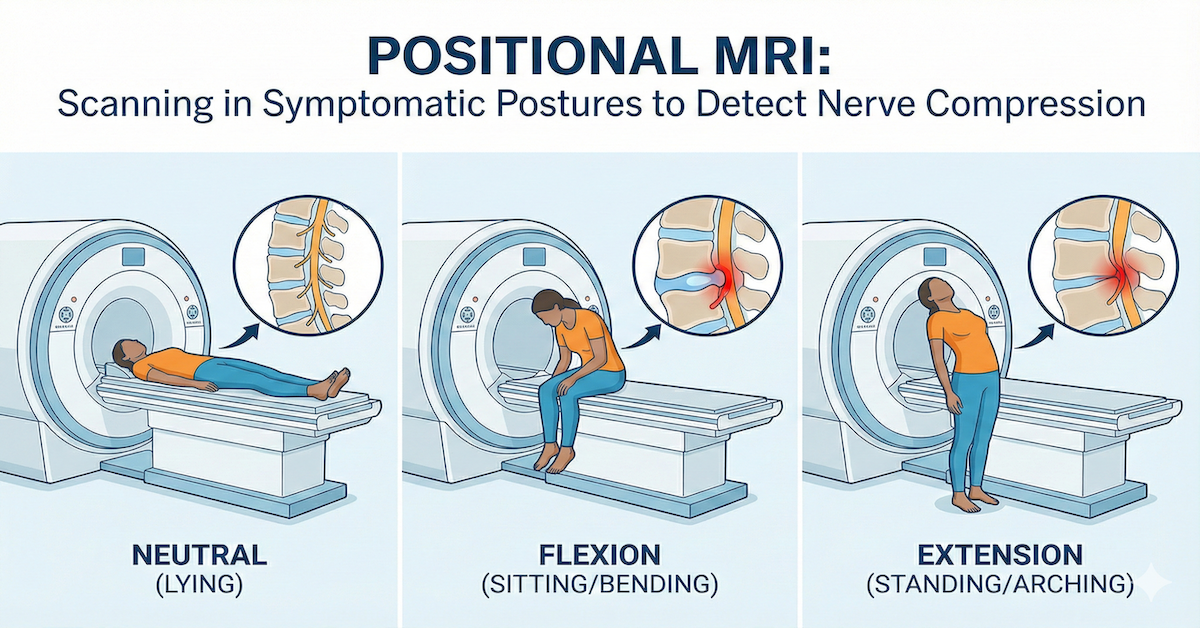
Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of spaces within the spine, putting pressure on the nerves.
- Central Canal Stenosis: Narrowing of the central spinal canal.
- Foraminal Stenosis: Narrowing of the openings where nerve roots exit the spine.
Spondylolisthesis: A condition where a vertebra slips out of place.
Spinal Cord and Nerve Root Issues: These can involve compression or inflammation, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness.
- Compression: When a disc or bone presses on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Inflammation: Swelling around the spinal cord or nerves.
Other potential findings include fractures, infections, and tumors, all of which require specific treatments.
Interpreting Specific MRI Results
Disc Abnormalities:
- Bulging vs. Herniated Discs: Bulging discs are still contained within the disc's outer layer, while herniated discs break through.
- Modic Changes: These are changes in the vertebral endplates seen on MRI, indicating degenerative disc disease.
Spinal Alignment and Curvature:
- Scoliosis: Abnormal lateral curvature of the spine.
- Lordosis and Kyphosis: Curvature of the spine in the lower back and upper back, respectively.
Soft Tissue and Ligament Issues:
- Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy: Thickening of the ligament that can contribute to spinal stenosis.
- Muscle Abnormalities: Changes or damage to the muscles around the spine.
Spinal Cord Conditions:
- Myelopathy: Dysfunction of the spinal cord, often due to compression.
- Syringomyelia: A cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord.
Importance of Clinical Correlation
An MRI is just one piece of the puzzle. Your healthcare provider will correlate MRI findings with your symptoms and physical exam results. This clinical correlation is crucial because not all abnormalities seen on MRI cause symptoms. Sometimes, an MRI may show issues that aren’t causing any problems.
Next Steps After MRI Results
After receiving your MRI results, the next steps typically involve discussing them with your healthcare provider. They will explain the findings in the context of your symptoms and medical history. Here are potential follow-up actions:
- Additional Tests: Sometimes, further imaging or tests are needed to clarify MRI findings.
- Treatment Options: Depending on the diagnosis, treatment can range from conservative management like physical therapy to interventional procedures or even surgery.
Conservative Management:
- Physical therapy
- Medications
- Lifestyle changes
Interventional Procedures:
- Injections (e.g., epidural steroid injections)
- Nerve blocks
Surgical Options:
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal fusion
Conclusion
Interpreting MRI back and spine results can be complex, but understanding the basics can help you have more productive discussions with your healthcare provider. By knowing what to look for and how to understand the report, you can make informed decisions about your treatment.
For expert MRI services and more, consider Upright MRI of Deerfield. We are dedicated to providing clear, detailed imaging to help you and your healthcare provider get to the root of your back and spine issues.
SHARE THIS POST:
Leave a Comment:

The World's Most Patient-Friendly MRI. A comfortable, stress-free, and completely reliable MRI scan. We offer patients an open, upright, standup MRI experience that helps those who are claustrophobic and stress being in a confined area. Upright MRI of Deerfield is recognized as the world leader in open MRI innovation,
Our Recent Post


READ PATIENT TESTIMONIALS
Upright MRI of Deerfield.
Susan D.,
Highland Park, 39
I am going to tell everyone about your office! This was a great experience after I panicked in other MRI machines and had to leave. Thank you so much.

Judith B.,
Milwaukee, 61
I suffer from vertigo and other MRIs do not work. This was wonderful…absolutely NO discomfort at all. The MRI was so fast…I wanted to stay and watch the movie! Mumtaz was great. His humor really put me at ease. I’ve already recommended Upright MRI to friends.

Delores P.,
Glencoe, 55
Everything is so nice and professional with your place. I have been there a couple of times. My husband and I would not go anywhere else.